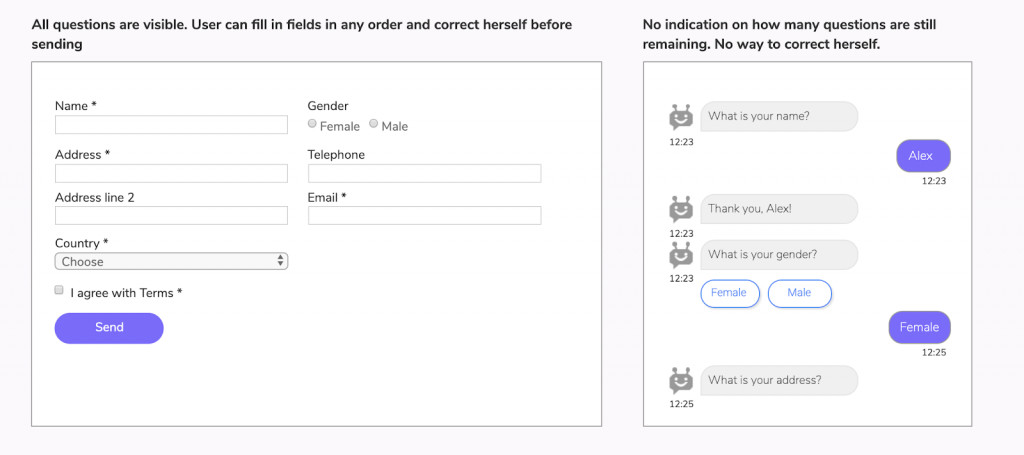
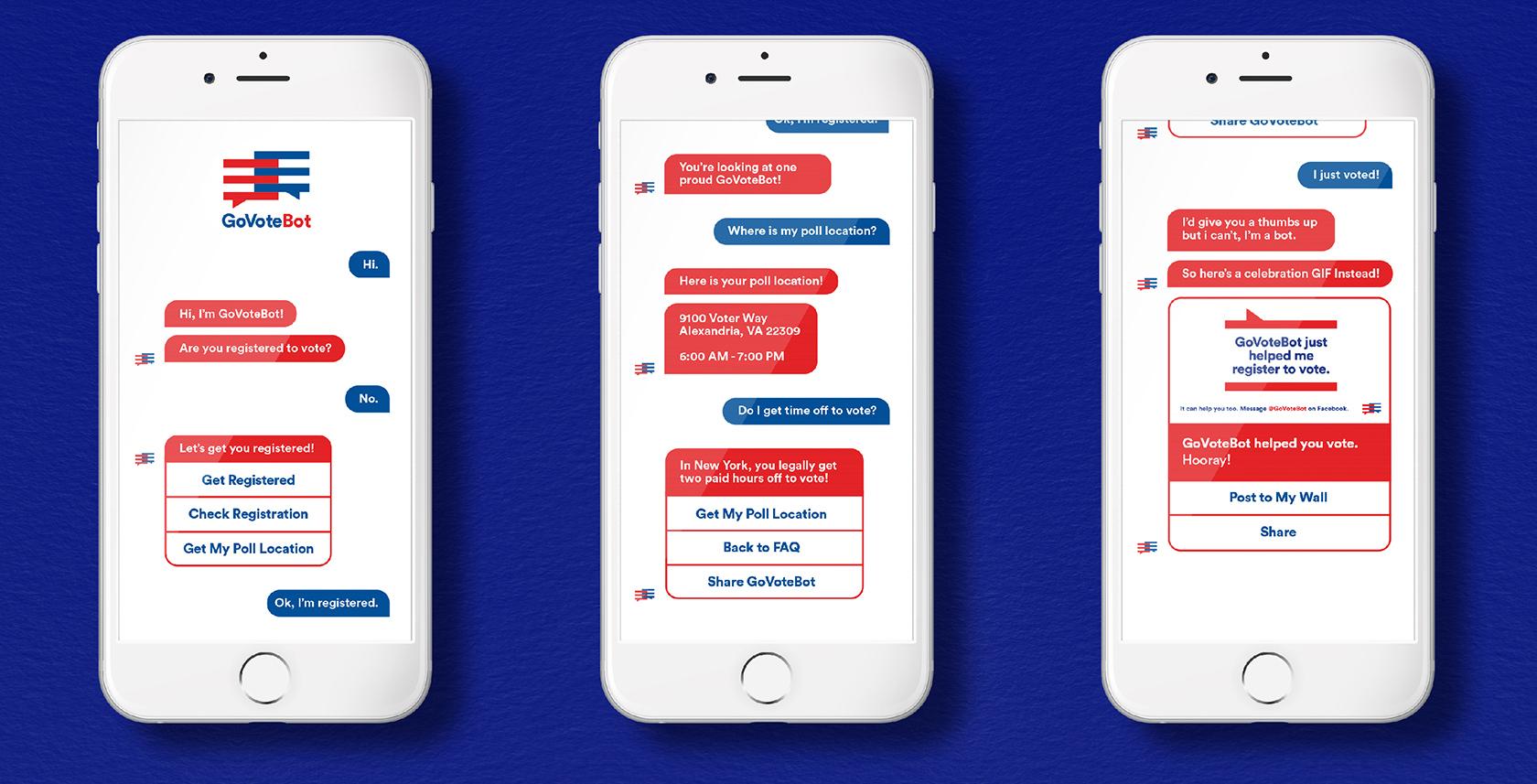
Form is way of communication
The content of this section is from Jessica Enders’ book, Design UX: Forms: Create Forms That Don’t Drive Your User Crazy (Aspects of UX)
Four-state Model for Question Answering
- Comprehension: understanding words and meaning
- Retrieval: searching memory, feelings, thoughts, and resources
- Judgement: checking answer suitability and making adjustments
- Answering: physically providing the answer.
Comprehension
Use plain language:
- shorter, simpler words
- shorter, simpler sentences, each of which expresses just one idea
- the active voice
- words that are familiar to the person filling out the form.


Avoid ambiguity
– “Where do you work?”
– “I work for Google.” or “I work in Fargo.” or “I work at home.”
Retrieval
Ask the questions that users can easily answer.
Judgement
Let the user know why you ask the questions. and provide instructions.
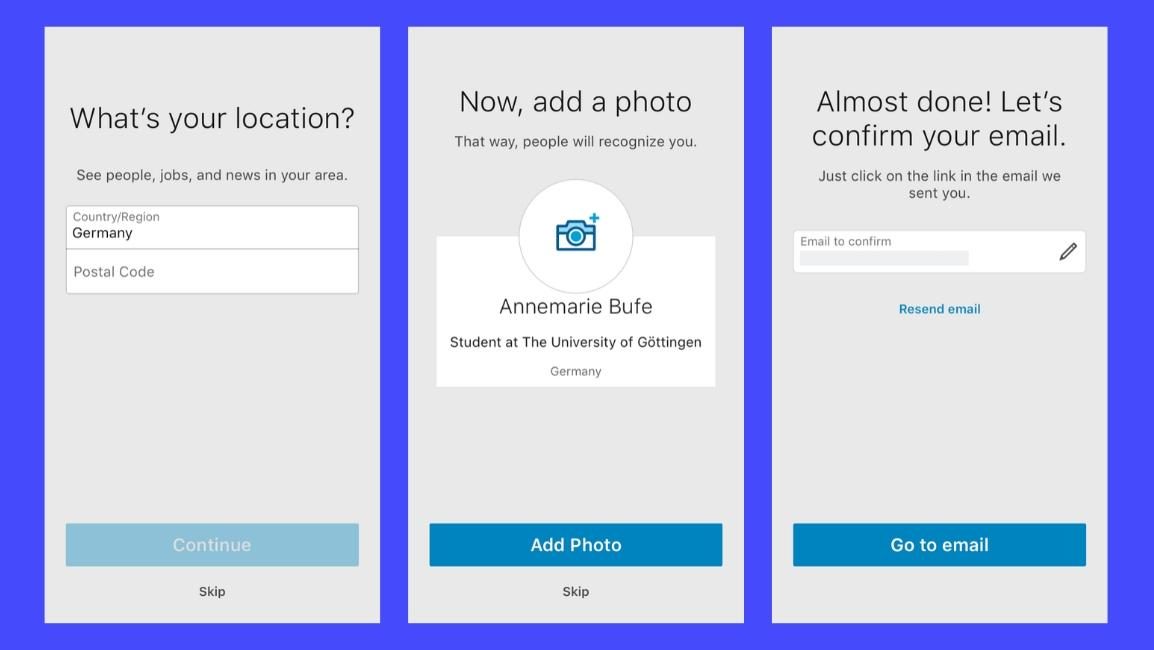
Create a welcome screen
This could be followed by an introduction page. If you put everything in one page. The user probably would not read the paragraphs.
Then start to tell the story
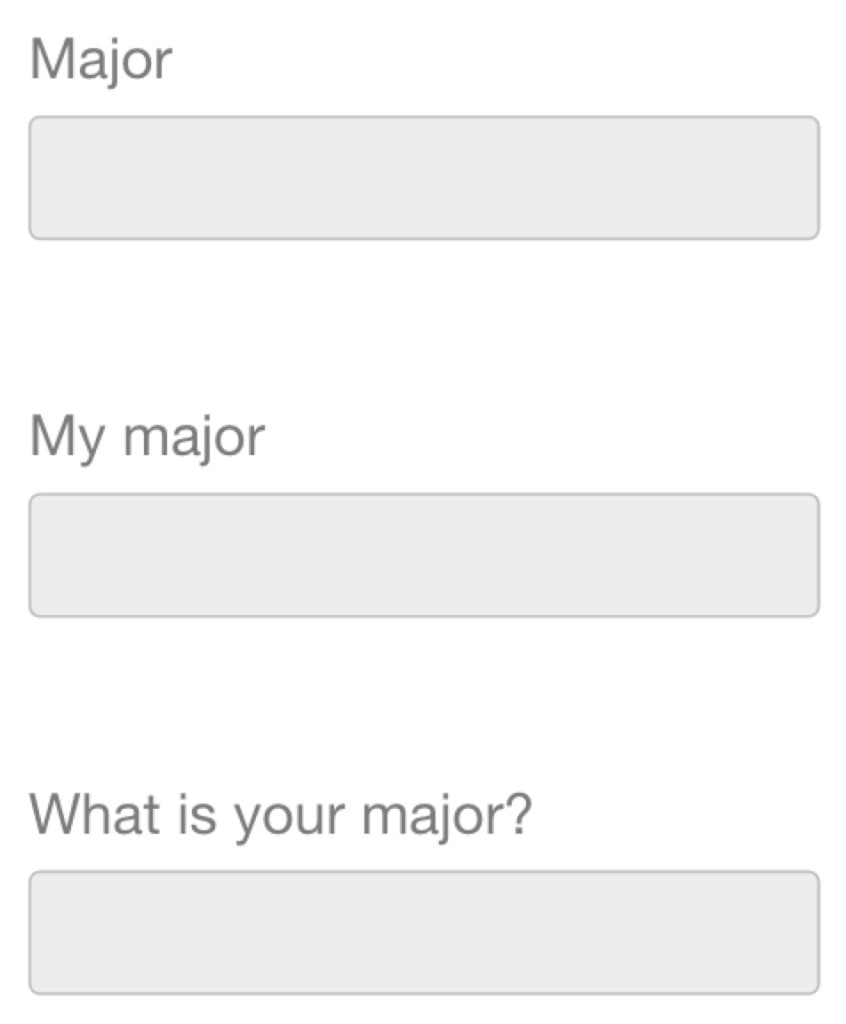
Yours or Mine?
What pronoun to use
Are your users telling their stories?
or
Are they having conversations with you?
Types of Forms
Stepper Form


Natural Language Form

Conversational Form